Probability with compound events worksheet provides an interactive and comprehensive exploration of the principles and applications of probability theory to compound events. By delving into the concepts of independent and dependent compound events, this worksheet empowers learners to master the techniques for calculating probabilities and apply them to real-world decision-making.
Probability plays a crucial role in diverse fields, from statistics and engineering to finance and risk management. Understanding how to calculate and interpret probabilities is essential for making informed decisions and solving complex problems. This worksheet provides a structured approach to understanding the fundamental principles of probability and their application to compound events.
1. Definition of Probability with Compound Events
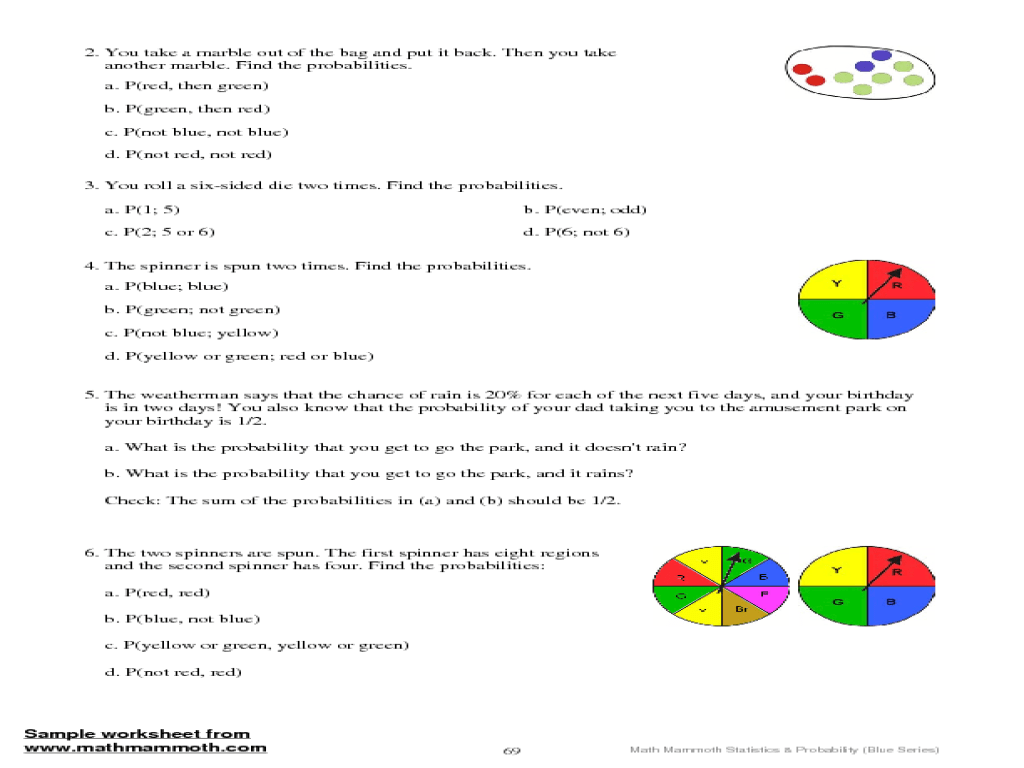
In probability theory, a compound event is an event that consists of two or more simpler events occurring together. The probability of a compound event is the likelihood that all of the individual events will occur simultaneously.
For example, consider the compound event of rolling a six on a die and then drawing an ace from a deck of cards. The probability of this event is the product of the probability of rolling a six (1/6) and the probability of drawing an ace (1/13), which is 1/78.
Compound events can be either independent or dependent. Independent events are those in which the occurrence of one event does not affect the probability of the other events. Dependent events are those in which the occurrence of one event does affect the probability of the other events.
2. Methods for Calculating Probability of Compound Events
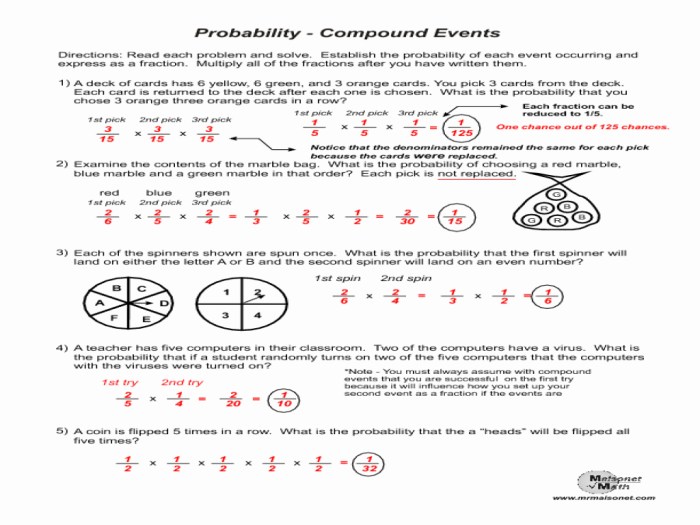
The Multiplication Rule is used to calculate the probability of independent compound events. The rule states that the probability of two independent events occurring together is the product of their individual probabilities.
For example, if the probability of rolling a six on a die is 1/6 and the probability of drawing an ace from a deck of cards is 1/13, then the probability of rolling a six and drawing an ace is 1/78.
The Conditional Probability Rule is used to calculate the probability of dependent compound events. The rule states that the probability of one event occurring given that another event has already occurred is equal to the probability of both events occurring divided by the probability of the first event occurring.
For example, if the probability of drawing a heart from a deck of cards is 1/4 and the probability of drawing an ace given that a heart has already been drawn is 1/13, then the probability of drawing a heart and then an ace is 1/52.
3. Applications of Probability with Compound Events

Probability with compound events is used in a wide variety of real-world applications, including:
- Statistics: Probability with compound events is used to calculate the probability of complex events, such as the probability of a particular outcome in a clinical trial.
- Engineering: Probability with compound events is used to design and test systems, such as bridges and airplanes.
- Finance: Probability with compound events is used to calculate the risk of investments and to make investment decisions.
4. Worksheet Design for Probability with Compound Events
An interactive worksheet can be designed to guide students through the concepts and calculations related to probability with compound events. The worksheet can include exercises that cover both independent and dependent compound events, and it can provide answer keys and detailed explanations for each exercise.
The worksheet can be used to help students learn about probability with compound events and to practice calculating the probability of these types of events.
FAQ Explained: Probability With Compound Events Worksheet
What is the difference between independent and dependent compound events?
Independent compound events are events where the occurrence of one event does not affect the probability of the other event occurring. Dependent compound events are events where the occurrence of one event affects the probability of the other event occurring.
How do I calculate the probability of an independent compound event?
To calculate the probability of an independent compound event, you multiply the probabilities of each individual event.
How do I calculate the probability of a dependent compound event?
To calculate the probability of a dependent compound event, you use the conditional probability rule. This rule states that the probability of an event A occurring given that event B has already occurred is equal to the probability of A multiplied by the probability of B given A.