Personal lines coverage extends only to single family dwellings – Personal lines coverage, a cornerstone of insurance policies, is exclusively tailored to single-family dwellings, excluding non-single-family properties. This distinction stems from underwriting risks and policy intent, with implications for policyholders and insurance professionals alike.
As we delve into the nuances of personal lines coverage, we will explore the definition of single-family dwellings, examine the reasons for coverage limitations for non-single-family dwellings, and identify alternative coverage options. Real-world examples and case studies will shed light on the practical implications of these coverage restrictions.
1. Personal Lines Coverage Scope

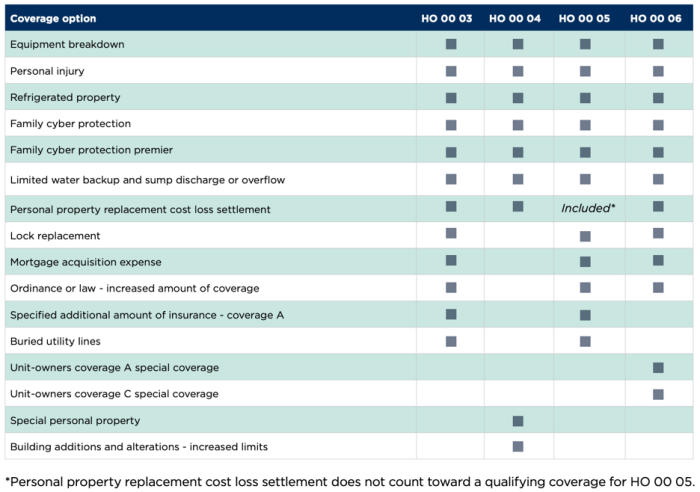
Personal lines coverage encompasses insurance policies designed specifically for individuals and families, providing protection for their personal assets and liabilities. It typically covers single-family dwellings, personal property, and various personal risks.
Personal lines policies generally include:
- Homeowners insurance: Covers the structure of the dwelling, personal belongings, and liability for accidents or injuries on the property.
- Renters insurance: Provides coverage for personal property and liability for renters in leased or rented dwellings.
- Automobile insurance: Insures vehicles owned by individuals, covering liability, collision, and other related risks.
- Personal liability insurance: Protects individuals from financial responsibility for bodily injury or property damage caused to others.
Limitations and exclusions in personal lines coverage may include:
- Coverage limits: Policies typically have limits on the amount of coverage provided for different perils.
- Deductibles: A deductible is a fixed amount that the policyholder must pay out-of-pocket before insurance coverage kicks in.
- Exclusions: Certain perils or situations may be specifically excluded from coverage, such as acts of war, earthquakes, or flooding.
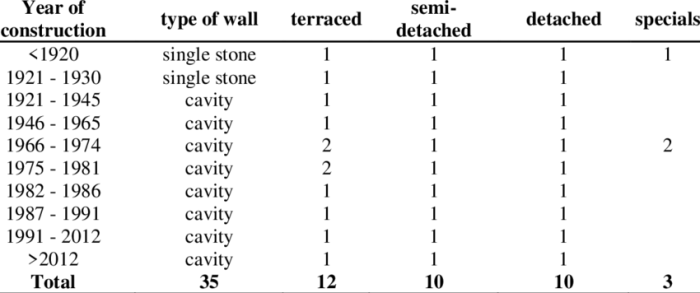
2. Single-Family Dwelling Definition
In the context of insurance policies, a “single-family dwelling” refers to a residential property that is designed and intended for the occupancy of a single family unit. It typically consists of a single structure on a single lot, with no attached or shared living spaces.
Properties that qualify as single-family dwellings include:
- Detached houses
- Townhouses with separate entrances and no shared walls
- Single-family condominiums or cooperatives
Exceptions or special considerations may apply to multi-family dwellings or commercial properties that are used for residential purposes. These properties may require specialized coverage options or endorsements to ensure adequate protection.
3. Coverage Limitations for Non-Single-Family Dwellings
Personal lines coverage typically excludes non-single-family dwellings due to the increased underwriting risks and policy intent.
Underwriting risks associated with non-single-family dwellings include:
- Increased potential for liability claims due to multiple occupants
- Higher likelihood of property damage or loss due to shared spaces and common areas
- Complex ownership structures and maintenance responsibilities
The policy intent of personal lines coverage is to provide protection for individual families and their personal assets. Non-single-family dwellings fall outside this scope due to their different risk profile and insurance needs.
Examples of situations where coverage may be limited or excluded for non-single-family dwellings include:
- Apartment buildings with multiple units
- Multi-family homes with shared living spaces
- Commercial properties used for residential purposes, such as bed and breakfasts or rental properties
Questions and Answers: Personal Lines Coverage Extends Only To Single Family Dwellings
What constitutes a “single-family dwelling” under personal lines coverage?
A single-family dwelling is a residential property designed and intended for occupancy by a single family or household, typically consisting of a detached house or townhouse.
Why is personal lines coverage limited to single-family dwellings?
Personal lines coverage is designed to address the specific risks associated with single-family dwellings, such as fire, theft, and liability. Non-single-family dwellings, such as multi-family units or commercial properties, pose different risks and require specialized coverage.
What are alternative coverage options available for non-single-family dwellings?
Alternative coverage options for non-single-family dwellings include landlord insurance for rental properties, commercial property insurance for businesses, and homeowners association (HOA) insurance for multi-family communities.