For proper operation instructions of the jointer: – As Proper Operation Instructions for the Jointer: takes center stage, this opening passage beckons readers into a world crafted with good knowledge, ensuring a reading experience that is both absorbing and distinctly original.
The content of the second paragraph that provides descriptive and clear information about the topic
Understanding Jointer Operation
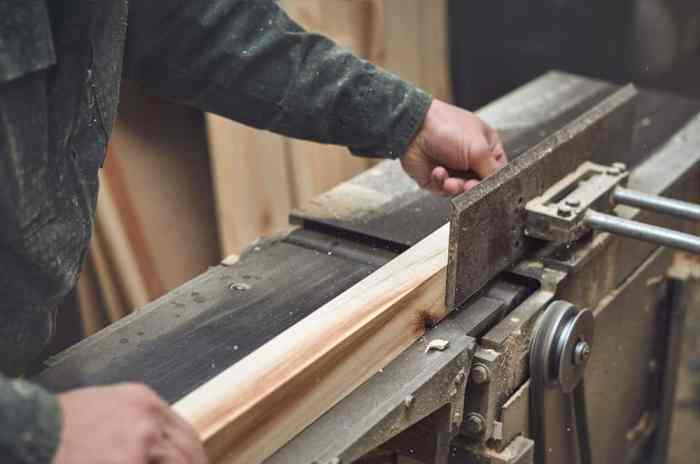

A jointer is a woodworking machine used to flatten and smooth the edges of boards or planks. It consists of a rotating cutterhead with multiple blades that remove material from the workpiece, creating a flat and even surface.
Types of Jointers, For proper operation instructions of the jointer:
- Benchtop jointers:Compact and portable, suitable for small-scale woodworking projects.
- Floor-standing jointers:Larger and more powerful, designed for heavy-duty applications in workshops and factories.
- Hand-held jointers:Small and lightweight, ideal for quick edge jointing or chamfering.
Jointer Components
Key components of a jointer include:
- Cutterhead:Rotating assembly with multiple blades that cut the workpiece.
- Infeed and outfeed tables:Support the workpiece as it passes through the cutterhead.
- Fence:Guides the workpiece along the desired path.
- Safety guards:Protect the operator from flying debris and accidental contact with the cutterhead.
Safety Precautions for Jointer Operation: For Proper Operation Instructions Of The Jointer:
Operating a jointer requires strict adherence to safety precautions to prevent injuries:
Essential Safety Measures
- Wear appropriate protective gear, including safety glasses, earplugs, and dust mask.
- Secure the workpiece firmly using clamps or hold-downs.
- Keep hands and fingers clear of the cutterhead and rotating parts.
- Never reach over the cutterhead to adjust the fence or workpiece.
- Use push sticks or blocks to guide the workpiece through the machine.
Safety Guards and Accessories
Safety guards and accessories play a crucial role in protecting the operator:
- Infeed and outfeed tables:Prevent accidental contact with the cutterhead.
- Fence:Guides the workpiece and prevents kickback.
- Blade guard:Covers the cutterhead, reducing the risk of contact.
- Anti-kickback fingers:Hold the workpiece down, preventing it from being thrown back.
Step-by-Step Jointer Operation

Follow these steps for safe and effective jointer operation:
Preparation
- Select the appropriate jointer for the task and workpiece size.
- Ensure the jointer is properly calibrated and in good working condition.
- Wear appropriate protective gear and secure the workpiece firmly.
Setup
- Adjust the fence to the desired width of the joint.
- Set the cutterhead height to slightly below the surface of the workpiece.
- Position the workpiece on the infeed table and align it with the fence.
Jointing Operation
- Power on the jointer and allow it to reach full speed.
- Use a push stick to guide the workpiece through the machine.
- Maintain a steady and even feed rate.
- Check the joint for flatness and smoothness.
Troubleshooting Common Jointer Problems
Common problems during jointer operation include:
| Problem | Troubleshooting Tips |
|---|---|
| Rough or uneven joint: | – Check cutterhead alignment and blade sharpness.
|
| Kickback: | – Ensure workpiece is firmly secured.
|
| Burn marks on workpiece: | – Reduce feed rate or cutterhead speed.
|
Advanced Jointer Techniques
Advanced jointer techniques allow for precise and professional-looking results:
Edge Jointing
Used to create perfectly square and straight edges on boards or planks. The workpiece is passed over the jointer with the edge against the fence, creating a flat and perpendicular surface.
Rabbeting
Creates a recess or groove along the edge of a workpiece. The workpiece is positioned on the jointer with the desired depth of the rabbet set on the fence.
Beveling
Produces angled edges on workpieces. The fence is tilted to the desired angle, and the workpiece is passed over the jointer to create a beveled edge.
Essential FAQs
What are the primary functions of a jointer?
A jointer is primarily used to flatten and straighten the edges of boards, making them suitable for joining.
What are the different types of jointers?
There are two main types of jointers: benchtop jointers and floor-standing jointers. Benchtop jointers are smaller and more portable, while floor-standing jointers are larger and more powerful.
What are the essential safety precautions to follow when operating a jointer?
Always wear appropriate safety gear, including eye protection, hearing protection, and a dust mask. Never operate a jointer with dull or damaged knives. Keep your hands away from the cutter head at all times.