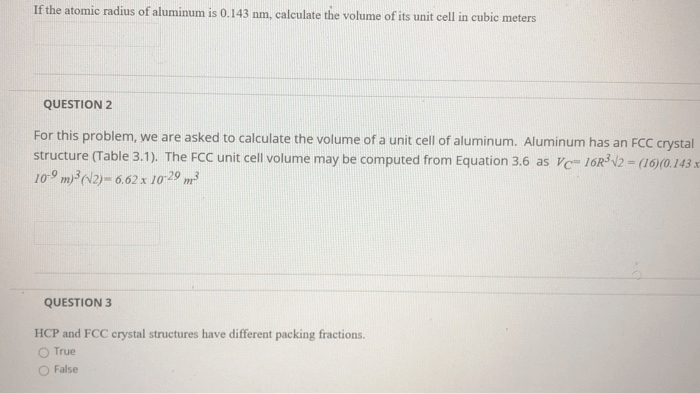
If the atomic radius of aluminum is 0.143 nm, it sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. Aluminum, with its unique atomic radius, plays a pivotal role in shaping its properties and applications, making it an indispensable element in various industries.
Delving into the depths of aluminum’s atomic radius, we will explore its significance in determining the element’s physical and chemical characteristics. Furthermore, we will investigate how these properties translate into practical applications, revolutionizing industries and shaping our modern world.
Atomic Radius of Aluminum
The atomic radius of an element is a measure of the distance from the nucleus to the outermost electron shell. It is a fundamental property that influences various chemical and physical properties of an element.
The atomic radius of aluminum is 0.143 nm. This value is determined by the number of electrons and protons in the aluminum atom. Aluminum has 13 electrons and 13 protons, giving it a neutral charge.
Factors Influencing Atomic Radius
- Number of electrons: As the number of electrons in an atom increases, the atomic radius generally increases. This is because the electrons occupy larger orbitals as their energy levels increase.
- Number of protons: The number of protons in the nucleus also affects the atomic radius. A greater number of protons increases the attraction between the positively charged nucleus and the negatively charged electrons, pulling them closer and reducing the atomic radius.
Comparison of Atomic Radii
| Element | Atomic Radius (nm) |
|---|---|
| Aluminum | 0.143 |
| Sodium | 0.190 |
| Magnesium | 0.160 |
| Silicon | 0.117 |
Properties of Aluminum: If The Atomic Radius Of Aluminum Is 0.143 Nm

The atomic radius of aluminum contributes to its unique physical and chemical properties.
Physical Properties
- Density: Aluminum has a relatively low density of 2.70 g/cm³, making it lightweight and suitable for applications where weight is a concern.
- Melting point: Aluminum has a low melting point of 660.32 °C, allowing it to be easily melted and cast into various shapes.
Chemical Properties
- Reactivity: Aluminum is a reactive metal that readily reacts with oxygen to form a protective oxide layer on its surface. This layer prevents further oxidation and enhances its corrosion resistance.
Applications of Aluminum, If the atomic radius of aluminum is 0.143 nm
- Aerospace: Aluminum’s lightweight and high strength make it ideal for aircraft and spacecraft components.
- Automotive: Aluminum is used in car bodies, wheels, and engine parts due to its weight reduction and fuel efficiency benefits.
- Construction: Aluminum is utilized in building facades, roofing, and window frames due to its durability and resistance to corrosion.
Comparison to Other Metals

| Metal | Atomic Radius (nm) | Density (g/cm³) | Melting Point (°C) | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | 0.143 | 2.70 | 660.32 | Aerospace, automotive, construction |
| Iron | 0.126 | 7.87 | 1538 | Construction, machinery, transportation |
| Copper | 0.128 | 8.96 | 1085 | Electrical wiring, plumbing, jewelry |
| Zinc | 0.139 | 7.14 | 419.5 | Galvanizing, batteries, alloys |
The smaller atomic radius of iron contributes to its higher density and strength, making it suitable for structural applications. Copper has a similar atomic radius to aluminum but a higher density, making it a good conductor of heat and electricity.
Zinc has a slightly larger atomic radius than aluminum, resulting in a lower density and a lower melting point. It is often used in galvanizing to protect steel from corrosion.
Commonly Asked Questions
What is the significance of the atomic radius of aluminum?
The atomic radius of aluminum plays a crucial role in determining its physical and chemical properties, such as density, melting point, and reactivity.
How does the atomic radius of aluminum affect its properties?
A smaller atomic radius generally leads to higher density, higher melting point, and increased reactivity.
What are the major applications of aluminum?
Aluminum finds extensive applications in aerospace, automotive, construction, and packaging due to its lightweight, strength, and corrosion resistance.